Introduction
The building sector in India is growing at a rapid pace and contributing significantly to the increase in energy demand. Increased usage of energy leads to higher green house gas (GHG) emissions and hence global warming. The green building movement in India, led by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), is helping reduce GHG emissions by improving energy efficiency in buildings and use of renewable energy sources partly for meeting energy requirements. Green buildings have demonstrated that about 25 to 30% reduction in energy consumption with respect to the national baselines can be achieved by implementing energy efficient measures and technologies. Further, depending upon the availability of space at the site and the cost economics, the green building concept encourages the deployment of onsite and off site
renewable energy sources to offset grid energy to the extent of about 10 to 15%.
The advancements in renewable energy technologies, policy interventions by the Government and the wider adoption of renewable resources have made the cost of renewable energy generation very competitive. In fact, buildings can become self-sufficient by generating their own energy requirements economically, through the use of onsite and off site renewable energy sources, which have now become a norm in the building industry. It is inspiring to witness, over the past few years, Shunya (net zero) initiatives being taken up in the country, which augurs well for a healthier and cleaner India.
IGBC Net Zero Energy Buildings Rating System
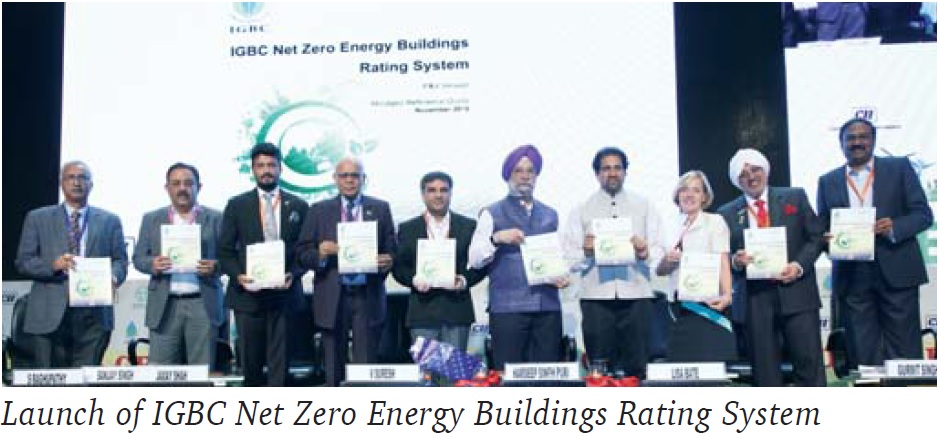
Taking forward the net zero initiatives in buildings, IGBC launched the ‘IGBC Net Zero Energy Buildings Rating System’ at Green Building Congress 2018 in Hyderabad. Hardeep Singh Puri, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Housing and Urban Affairs, released the rating system at the inaugural session of the Congress.
This rating system is a tool that enables the designer to apply energy efficiency measures and suggest the deployment of appropriate renewable sources by design to construct a Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB).
In case of an existing building, the tool enables implementation of energy efficiency measures to reduce the overall energy demand of the building or project, and to integrate the renewable energy system to off set the remaining energy requirement. The net zero energy buildings rating system has adhered to Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) 2017 to drive energy efficiency in buildings, by achieving compliances such as ECBC Compliance, ECBCPlus and SuperECBC. A SuperECBC compliant project can be defi ned as approaching net zero, where further integration of resources would support the building project to achieve net zero status. The NZEB is a concept by IGBC to drive market transformation in energy efficiency of buildings; it also supports WorldGBC’s global project aiming to promote and support the acceleration of net zero carbon buildings to 100% by 2050.
Addressing National Priorities
The rating system complements the National Mission on Enhanced Energy Efficiency and National Solar Mission, and supports the Government in achieving the set targets. It addresses the following national priorities:
• Reducing the national energy demand by enhancing energy effi ciency.
• Increasing the contribution of renewable energy sources for meeting the energy demand.
• Reducing the use of fossil fuels.
• Ultimately reducing GHG emissions to meet our international commitments.
Features
IGBC Net Zero Energy Buildings Rating System is a voluntary and consensus-based programme. The objective of the System is to facilitate a holistic approach to make energy efficient buildings fully powered by renewable energy sources. The rating system evaluates buildings on a performance-based approach. The rating system has evolved to be comprehensive and at the same time user-friendly. The programme is fundamentally designed to reduce the energy needs of a building and address the national priorities.
Scope
The Rating System is designed for both new and existing buildings, for air-conditioned and non-air-conditioned buildings. These buildings include (but are not limited to) offices, IT parks, Indian Railways, institutions, banks, hotels, hospitals, airports, convention centres, educational institutions, factory buildings, and schools.
Benefits
The Rating System enables signifi cant reduction in energy consumption and use of appropriate renewable energy sources to meet the energy requirement of the building project. The benefits of adopting this concept in a building include the following:
• Signifi cant improvement in energy efficiency and hence reduction in annual energy consumption to the tune of about 40% with respect to the national baseline.
• Overall reduction in operational cost.
• Maximising the use of renewable energy sources.
• National and international energy benchmarking.
• Recognition at national and global level.
Projects registered so far under IGBC Net Zero Energy Buildings Rating System include the following:
• Hindustan Zinc Limited, Udaipur
• Capgemini, Bangalore
• Shairu Gems Diamond Factory, Surat
• RSETI - ICICI Bank, Jodhpur
• PL-13 A, Godrej & Boyce, Mumbai
• Globicon Terminals, Mumbai
It is learnt that Cochin international airport is striving towards renewable energy generation to not only meet its own energy needs but also be net positive to give back to the grid.
Disclaimer: The information provided within this publication / eBook/ content is for general informational purposes only. While we try to keep the information up-to-date and correct, there are no representations or warranties, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the information, products, services, or related graphics contained in this publication / eBook/ content for any purpose. Any use of this information is at your own risk.
 Youth
Youth
 Women
Women
 Research for Ishrae
Research for Ishrae